Reaserch Topics
(1) Synthesis and biological evaluation of bioligically active natural products and theri derivatives
(1-A) Synthesis and biolgical evaluation of carbohydrates involved in self-nonself recognition
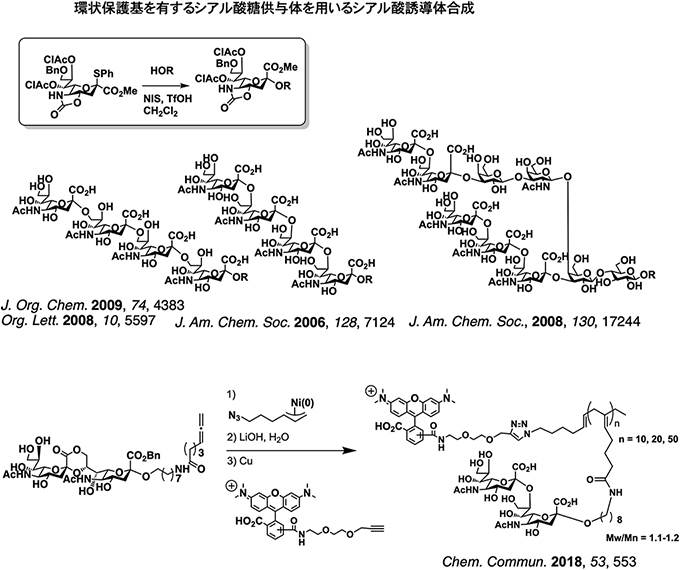
(1-A-I) Sialo-conatining oligosaccharides
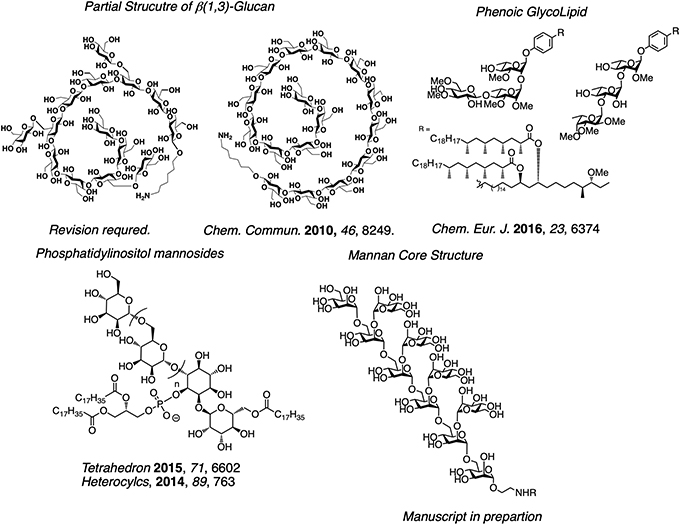
(1-A-II) Carbohydates on pathogenic fungus surface
(1-B) Bioligically active compounds contained in functional Foods
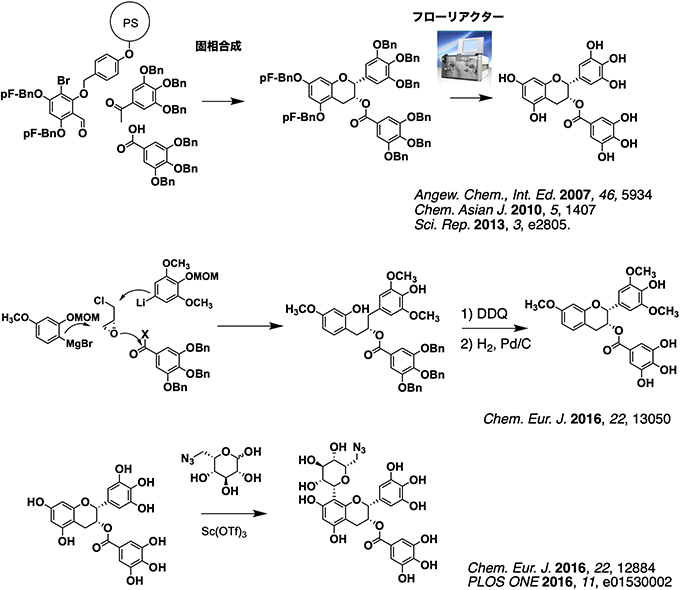
(1-B-I) Polyphenols
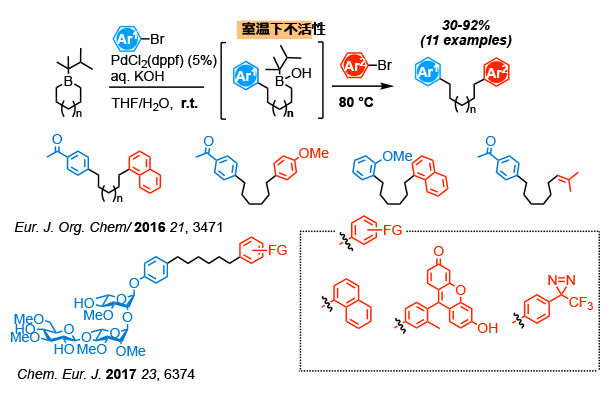
(2) Cyclic boron compounds as multifunctional platform for organic synthesis
(3) Development of radio-theranostics utilizing radioactive halogens
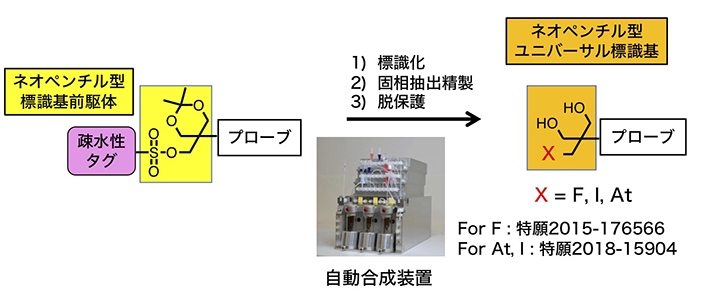
(3-A) Universal radioactive halogenating units
(3-B) Deverlopment of autometed syntheirzer
(1) Synthesis and biological evaluation of bioligically active natural products and theri derivatives
(1-A) Synthesis and biolgical evaluation of carbohydrates involved in self-nonself recognition
A variety of complex carbohydrates on the surface of cells are often used as targeting factors of immune cells by being used as an indicator of self-nonself identification. Therefore, these sugar chains are expected to function as immunomodulatory molecules, anticancer agents, antiallergic agents, and antibacterial agents. Our laboratory mainly focuses on sialic acid-containing sugar chains functioning as human self-markers and complex carbohydrates contained in pathogenic bacteria that sell immunity activating and suppressing actions, and the method of synthesis We are promoting development and functional evaluation.
(1-A-I) Sialo-conatining oligosaccharides
Sialic acid is a 9 monosaccharide having a carboxylic acid, which is present at the nonreducing end of the sugar chain and plays an important role in the interaction between the sugar chain and the biomolecule. Therefore, it is required to develop efficient methods for the synthesis of sialo-contaiing oligosaccharides and the chemical probes to modulate interaction between biopolymers with sialic acid. We have found that a sialy donor having a strained pyran ring by a cyclic protecting group shows high reactivity and desired stereoselectivity. Furthermore, by utilizing this method, a complex ganglioside sugar chain ( GP1c) has been achieved. Furthermore, we also prepared glycopolymers possessing disialic acids as pendants were prepered by nickel-catalized polymerization of allene glyco-allene monomers, and elucidate their inhibitory effect on interaction of solid-supporte disialic acid and receptor (Siglec-7).
(1-A-II) Carbohydates on pathogenic fungus surface
Carobohydates on a pathogenic fungus surface are recognized by immune systems and induce immun responces. In addition, fungi with very high pathogenicity contain carbohydates suppressing immune responce. Chemical synthesis and biological evaluation of structurely definded carbohyrate derivatives strongly can assisit to develop lead compounds as antiallergy, anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer drugs. We have projects invilving the synthesis and bioligical evaluation of partial structure of polysaccharide β glucan having an immunoactivating actiivty, partial structure of lipomannan mannan on the surface of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and glycolipid (PGL) having immunosuppressive activity.
(B) Bioligically active compounds contained in functional Foods
Food is a generic term for a group of substances that we decided to be able to take in our own body. Therefore, elucidation of a influence of compounds contained in foods on the our body is important not only for elucidating the biological mechanism but also for deepening the basic understanding for promoting health. However, most food ingredients are mixtures of structural analogs and it is difficult to clarify the function of each compound. Therefore, by chemically synthesizing food ingredients and their analogues, we aim to elucidate their functions and create new functional molecules.
(1-B-I)Polyphenols
Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) is a polyphenol contained in green tea and exhibits various biological activities. Our laboratory aims at elucidating the structure-activity relationship of EGCG and creating a functional molecule based on EGCG. We have synthesized a combinatorial library of methylated EGCG using solid-phase synthesis and microflow reactor. Biological evaluation of the library shows that the phenols of A ring can be modified without reduction of their bioligical activity. In addition, we estalihsed a methodo for the synthesis of opitically active EGCG derivatives by using epichlorohydrin as a chiral pool. Futhermore, we developed a bifunctional linker based on idose, a stereoisomer of glucose, and developed a one-step modification method for A ring of EGCG.
(2) 環状ホウ素化合物を多機能プラットフォームとして利用する有機合成
Boron compounds can be combined with transition metal catalysts to enable various coupling reactions. The Suzuki-Miyaura reaction using a palladium catalyst is one of the most utilized reactions in the synthesis of functional molecules. Our laboratory is develop one-pot sequentical coupling reaction of cyclic boron compounds. A cyclic borane is converted to acyclic boric acid via Suzuki-Miyaura reaction. The boric acid is further reactable with a different electrophile to provide a compound asymmetrically modified. By thes method, synthesis of PGL derivatives has been achieved.
(3)Development of radio-theranostics utilizing universal radioactive halogenating units
Theranostics is a word expressing the fusion of therapy and diagnosis. Radio-therastostics is a technique for achieving treatment and diagnosis with compounds of the same skeleton using radionuclides of different properties. For example, 18 F is one of positron emitting nuclides, enabling high resolution image diagnosis. On the other hand, 211 At is a short-range α-ray emitting nuclide and is thought to enable radiotherapy with few side effects . In our laboratory, we are developing a radiotheranostic technology based on our unique univeral radioactive halogenating unit which can efficiently introduce all these radioactive halogens and is stable in vivo. We are also developing an automated synthesizer for preparation of radioactive compounds safety and reproducively.